<!DOCTYPE html>
Understanding Sudden Encephalitis: A Comprehensive GuideWhat is Sudden Encephalitis?
Sudden encephalitis refers to an inflammation of the brain that occurs rapidly and can lead to severe neurological symptoms. It is a rare but serious condition that can affect individuals of all ages, though it is more common in children. The inflammation can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, or other underlying conditions.
Causes of Sudden Encephalitis
The most common cause of sudden encephalitis is viral infections, such as the herpes simplex virus (HSV), enteroviruses, and influenza viruses. However, other pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and parasites, can also trigger the condition. In some cases, the exact cause of encephalitis remains unknown, leading to the term "idiopathic encephalitis." Autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome, can also cause inflammation of the brain.
Symptoms of Sudden Encephalitis
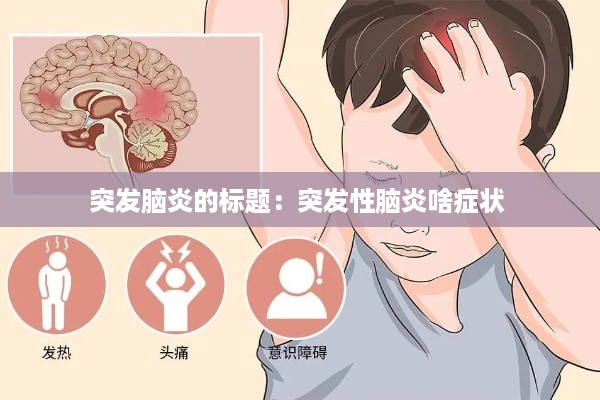
The symptoms of sudden encephalitis can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and the extent of brain inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe muscle weakness or paralysis
- Confusion and altered consciousness
- Seizures
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Loss of coordination or balance
These symptoms can progress rapidly, and in some cases, they can lead to life-threatening complications, such as brain swelling (encephalomalacia) or coma.
Diagnosis of Sudden Encephalitis
Diagnosing sudden encephalitis can be challenging due to the broad range of possible causes and the non-specific nature of symptoms. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. diagnostic tests may include:
- Neurological examination to assess cognitive function, muscle strength, and reflexes
- Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, to visualize the brain and detect any abnormalities
- Laboratory tests, including blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, and viral culture, to identify the causative agent
In some cases, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be necessary to collect CSF for analysis. This procedure can help identify infections, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
Treatment of Sudden Encephalitis
The treatment of sudden encephalitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Antiviral medications are often prescribed for viral encephalitis, while antibiotics may be used for bacterial infections. Antifungal agents or antiparasitic drugs may be necessary for fungal or parasitic infections, respectively. In some cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation and prevent brain swelling.
Supportive care is also crucial, including the management of symptoms, such as fever, seizures, and nausea. In severe cases, patients may require intensive care, including mechanical ventilation and intravenous fluids. Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be necessary after recovery to help regain lost function.
Prevention and Outlook
Preventing sudden encephalitis involves avoiding exposure to known risk factors. For example, vaccination against certain viruses, such as herpes simplex virus or influenza, can help reduce the risk of developing encephalitis. Good hygiene practices, such as handwashing and avoiding exposure to infected individuals, can also help prevent viral infections.
The outlook for individuals with sudden encephalitis varies widely. Some patients may recover completely, while others may experience long-term neurological deficits. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes. Researchers continue to study encephalitis to improve understanding and treatment options.
Conclusion
Sudden encephalitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms,
转载请注明来自山东高考日语培训,日本留学,枣庄日语培训机构,本文标题:《突发脑炎的标题:突发性脑炎啥症状 》








 蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
还没有评论,来说两句吧...